New
CUPRAC antioxydant capacity
Reference : KF01005
CUPRAC antioxidant capacity assay kit
Countries eligible for delivery
Countries eligible for delivery:
France (except Corsica and overseas departments and territories), Belgium, French overseas departments and territories, French Polynesia, Luxembourg, Switzerland, France (Corsica)
CUPRAC (CUPric Reducing Antioxidant Capacity) is a mostly new method which, for example, enables TAC measures even in oils.
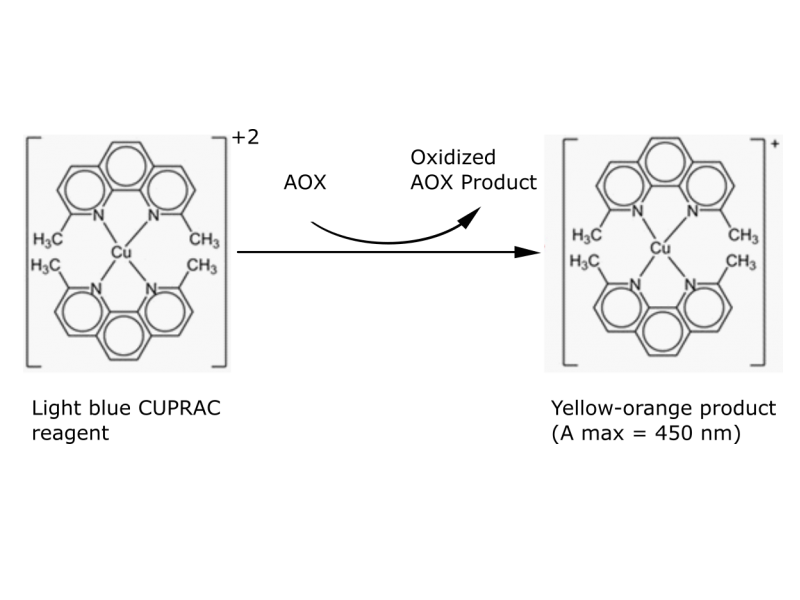
The main reagent, the copper (II)-neocuproin (2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline), can oxidize antioxidants generating a coloured product measurable by colorimetric methods. The chelation with neocuproin enables a fastened reaction by elevating the redox potential of the reagent.
Recent correlations have been saw within many illnesses and ROS (reactive species of oxygen, as superoxide); antioxidants on the other hand have been proved to inhibit this ROS. So the measure of these antioxidants seems an interesting new approach to study not only illnesses, also many other physiological states.
Assay Principle
CUPRAC reagent implies an oxidation of an antioxidant with a leading tiol group, like for example gluthation (GSH). In this process, the reagent reduces itself forming a chelate complex of cupper (I) – neocuproin, wich provides color measurable at 450nm in a spectrophotometer. This reaction takes place on physiological pH (or neutral pH, near pH 7).
The main reagent, the copper (II)-neocuproin (2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline), can oxidize antioxidants generating a coloured product measurable by colorimetric methods. The chelation with neocuproin enables a fastened reaction by elevating the redox potential of the reagent.
Recent correlations have been saw within many illnesses and ROS (reactive species of oxygen, as superoxide); antioxidants on the other hand have been proved to inhibit this ROS. So the measure of these antioxidants seems an interesting new approach to study not only illnesses, also many other physiological states.
Assay Principle
CUPRAC reagent implies an oxidation of an antioxidant with a leading tiol group, like for example gluthation (GSH). In this process, the reagent reduces itself forming a chelate complex of cupper (I) – neocuproin, wich provides color measurable at 450nm in a spectrophotometer. This reaction takes place on physiological pH (or neutral pH, near pH 7).
Biological samples (hydrophilic and hydrophobic)
Notice CUPRAC - kit de dosage.pdf
The attached documents are subject to change. To receive the latest updates, please contact us.
Specifications
| Reference | Packaging | |
|---|---|---|
| KF01005-100 | 100 tests (96 puits/wells format) | |
| KF01005-200 | 200 tests (96 puits/wells format) | |
| KF01005-400 | 400 tests (96 puits/wells format) |